How Aircraft Fly In The Air
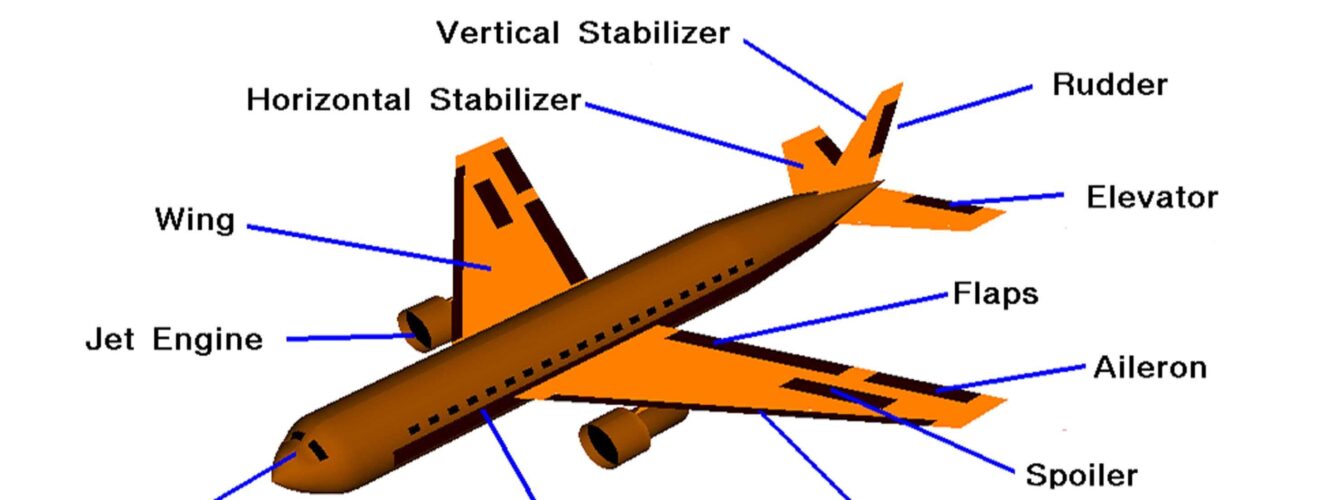
The flight of an airplane involves principles of aerodynamics, which is the study of the behavior of air as it interacts with solid objects, such as the wings and fuselage of an aircraft. There are four fundamental aerodynamic forces that contribute to the flight of an airplane:
Lift:
Lift is the force that enables an airplane to rise off the ground. It is generated by the wings as air flows over and under them. The shape of the wing (airfoil) is designed to create a pressure difference, with lower pressure above the wing and higher pressure below. This pressure difference results in an upward force called lift.
Gravity (Weight):
Gravity acts downward, pulling the airplane toward the Earth. The weight of the aircraft must be balanced by the lift generated by the wings to achieve and maintain level flight.
Thrust:
Thrust is the forward force produced by the aircraft’s engines. It counteracts the drag (air resistance) that opposes the airplane’s forward motion. To initiate and sustain flight, the thrust must be greater than the drag.
Drag:
Drag is the aerodynamic resistance that opposes the forward motion of the airplane. Pilots and engineers work to minimize drag to improve the efficiency of the aircraft. Streamlining the shape of the airplane and its components helps reduce drag.
The basic process of flight involves the airplane moving forward through the air, with the wings generating lift, and the engines providing the necessary thrust to overcome drag and maintain forward motion. The control surfaces, including ailerons, elevators, and rudders, allow the pilot to control the orientation and direction of the aircraft.
The specific design of an aircraft, including the wing shape, engine placement, and control surfaces, is carefully engineered to optimize its aerodynamic performance. The principles of flight are described by Bernoulli’s principle, which explains the relationship between air pressure and the speed of air molecules.
It’s important to note that the explanation provided here is a simplified overview of the complex aerodynamics involved in flight. The field of aviation involves in-depth engineering, physics, and fluid dynamics to design and operate safe and efficient aircraft.








