Ancient Egyptian facts


Ancient Egypt stands as an extraordinary chapter in the annals of human history. With a civilization dating back thousands of years, this land along the Nile River unveils tales of pharaohs, pyramids, and a rich tapestry of cultural achievements. From the monumental Pyramids of Giza to the mystical allure of the Sphinx, the ancient Egyptians left an indelible mark on architecture, art, and spirituality. In this exploration, we unravel the mysteries of this fascinating civilization, delving into the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms, deciphering hieroglyphics, and rediscovering the echoes of gods and pharaohs that resonate through the corridors of time.
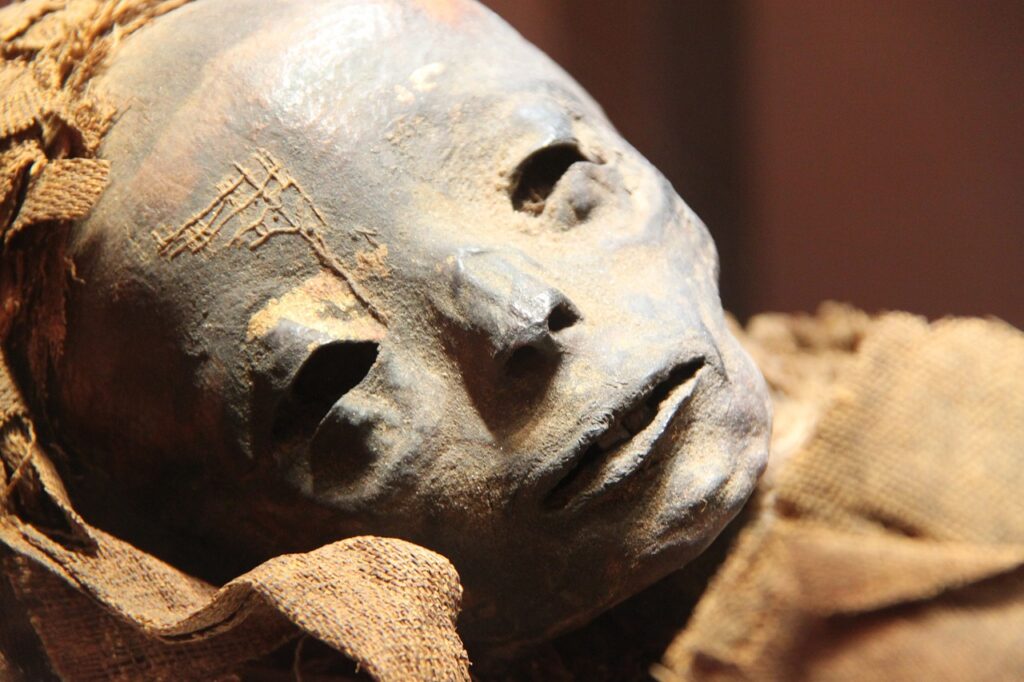

Certainly! Here are some more specific facts about ancient Egypt:-
Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms: Ancient Egyptian history is often divided into three main periods known as the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom. Each period had its own set of pharaohs, achievements, and cultural developments.
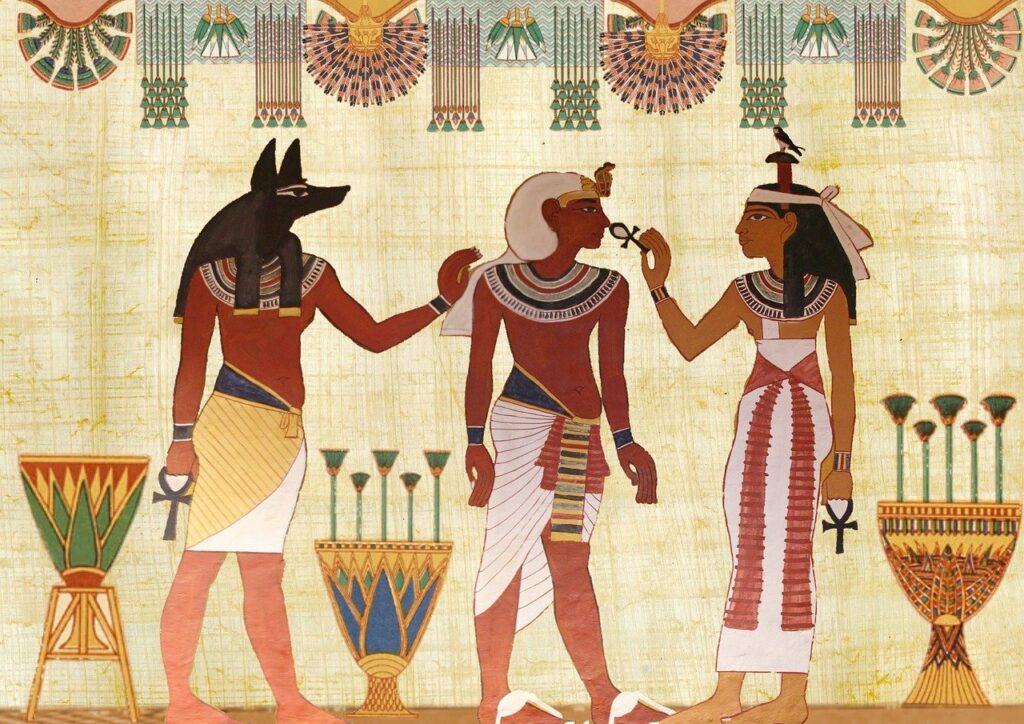


Old Kingdom (c. 2686–2181 BCE): This era is best known for the construction of the Pyramids of Giza, including the Great Pyramid built for Pharaoh Khufu.
Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BCE): The Middle Kingdom is characterized by the reunification of Egypt after a period of fragmentation. It saw the construction of temples and the development of literature, including religious texts.
New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BCE): This was a period of military conquests and imperial expansion. Pharaohs like Thutmose III and Ramses II played significant roles in building the Egyptian Empire.
Akhenaten and Atenism: Pharaoh Akhenaten, during the New Kingdom, introduced a brief religious revolution by promoting the worship of the sun disc, Aten. This period is known as the Amarna Period.

Hatshepsut: Queen Hatshepsut was one of the few female pharaohs in ancient Egypt. She is known for her temple at Deir el-Bahari and her trade expeditions to the Land of Punt.
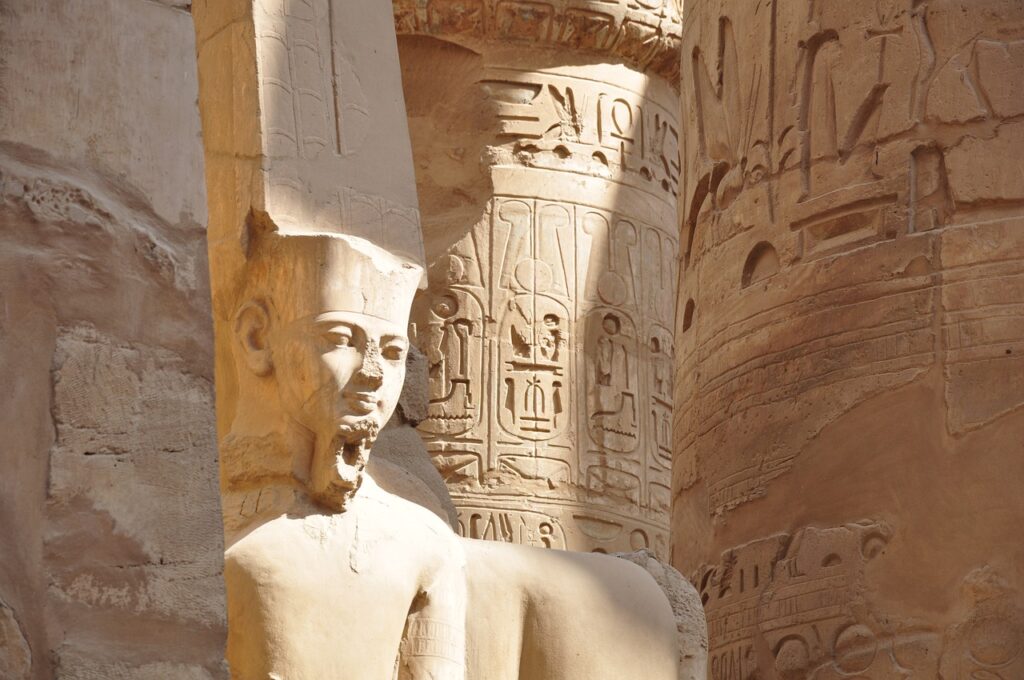
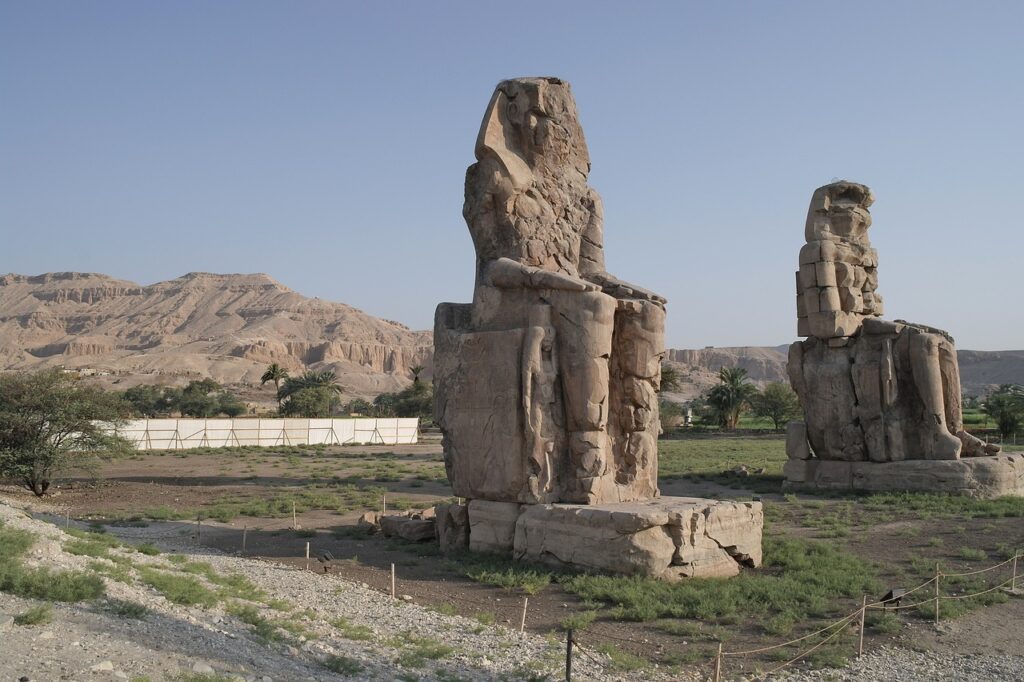
Valley of the Kings: Located on the west bank of the Nile near Luxor, the Valley of the Kings served as a burial site for many pharaohs of the New Kingdom, including Tutankhamun.
Temples of Karnak and Luxor: These temples, located in the ancient city of Thebes, are among the largest religious complexes in the world. They were dedicated to various deities and served as important religious and political centers.

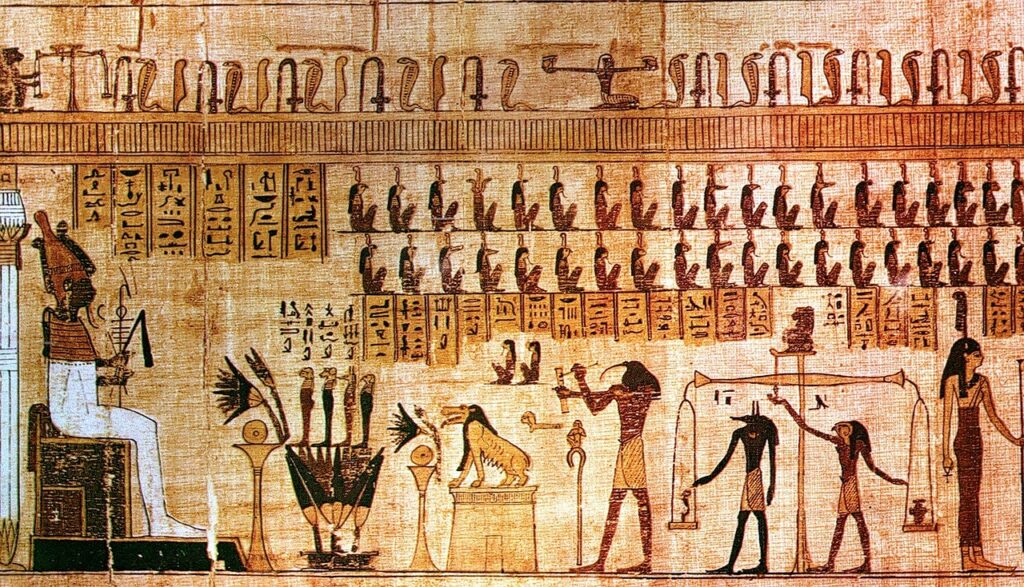
Book of the Dead: This funerary text was used in burials to guide the deceased through the afterlife. It contained spells, prayers, and illustrations to help the soul navigate challenges in the underworld.
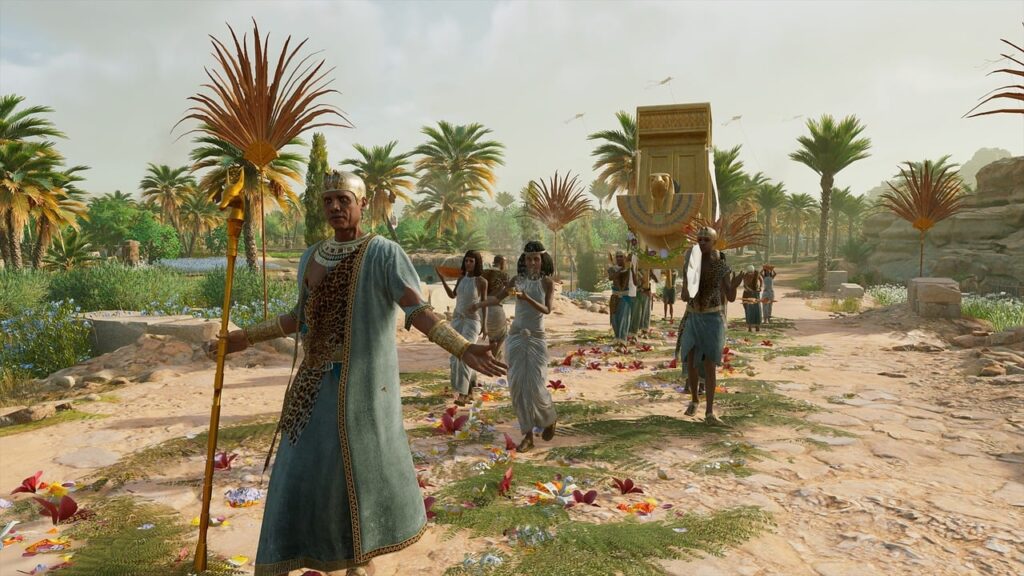


Trade and Commerce: Ancient Egypt engaged in trade with neighboring regions, such as Nubia, the Levant, and the Mediterranean. Egyptian goods, including papyrus, gold, and linen, were highly sought after.
Engineering and Architecture: The ancient Egyptians were skilled engineers and builders. Apart from the pyramids, they constructed impressive temples, obelisks, and irrigation systems like the Qanat system.
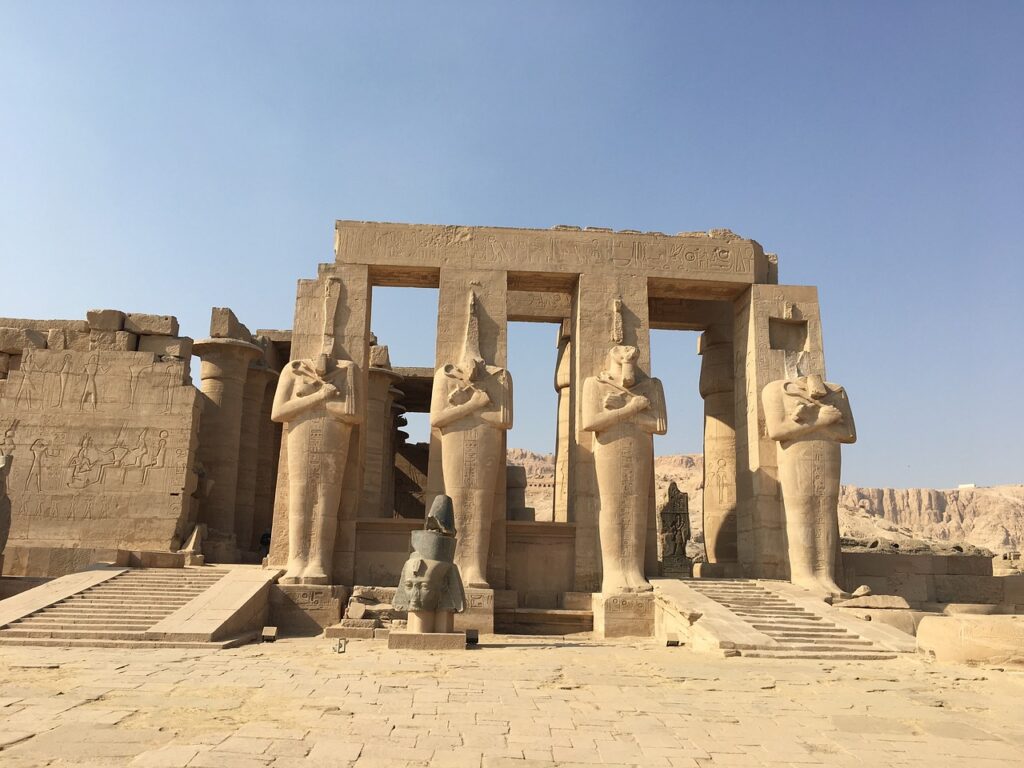

These facts provide a glimpse into the diverse and fascinating history of ancient Egypt.








