Knows ‘China History’ from Ancient to Modern life

China, an ancient civilization steeped in history, boasts a legacy that spans thousands of years. From the mythological origins of the Xia Dynasty to the mighty dynasties like Qin, Han, Tang, and Ming, its historical tapestry weaves together tales of innovation, cultural richness, and societal transformation. Through periods of imperial rule, foreign invasions, and revolutionary changes, China’s story is one of resilience, evolution, and enduring traditions. This vast and diverse history has sculpted China into the powerhouse it is today, blending ancient heritage with modern ambitions on the global stage.
Chinese history spans thousands of years, making it one of the oldest continuous civilizations in the world. Its history is typically divided into several major periods.
Ancient China
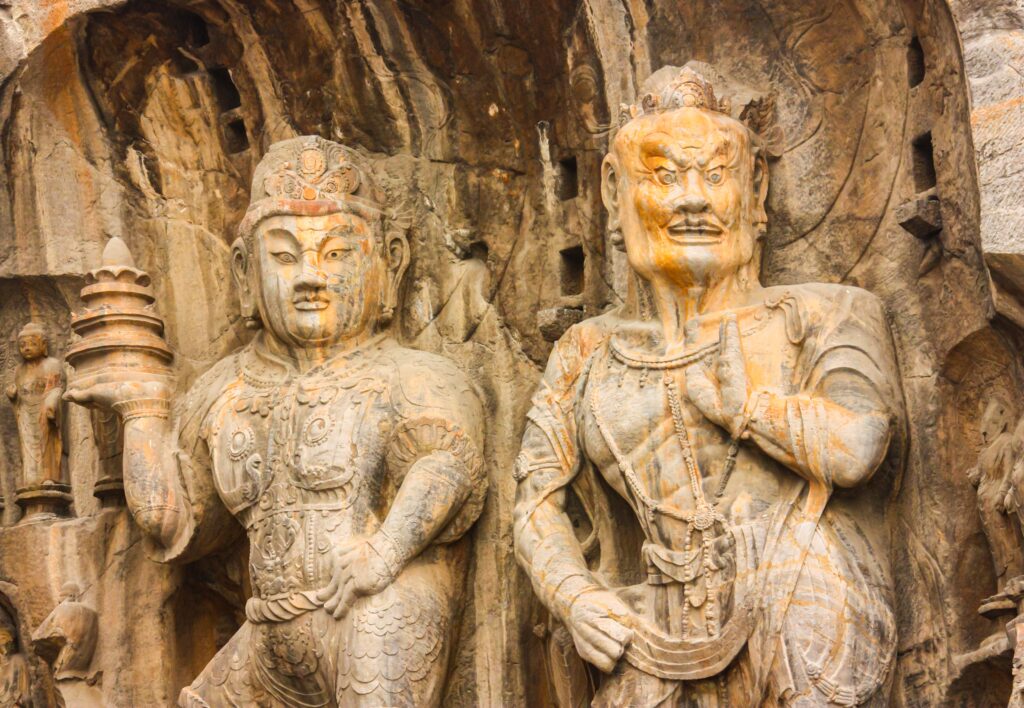




This period dates back to around 2000 BC with the Xia Dynasty, though historical records from this era are more mythological than factual. The Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BC) is the earliest historically confirmed dynasty.
Imperial China
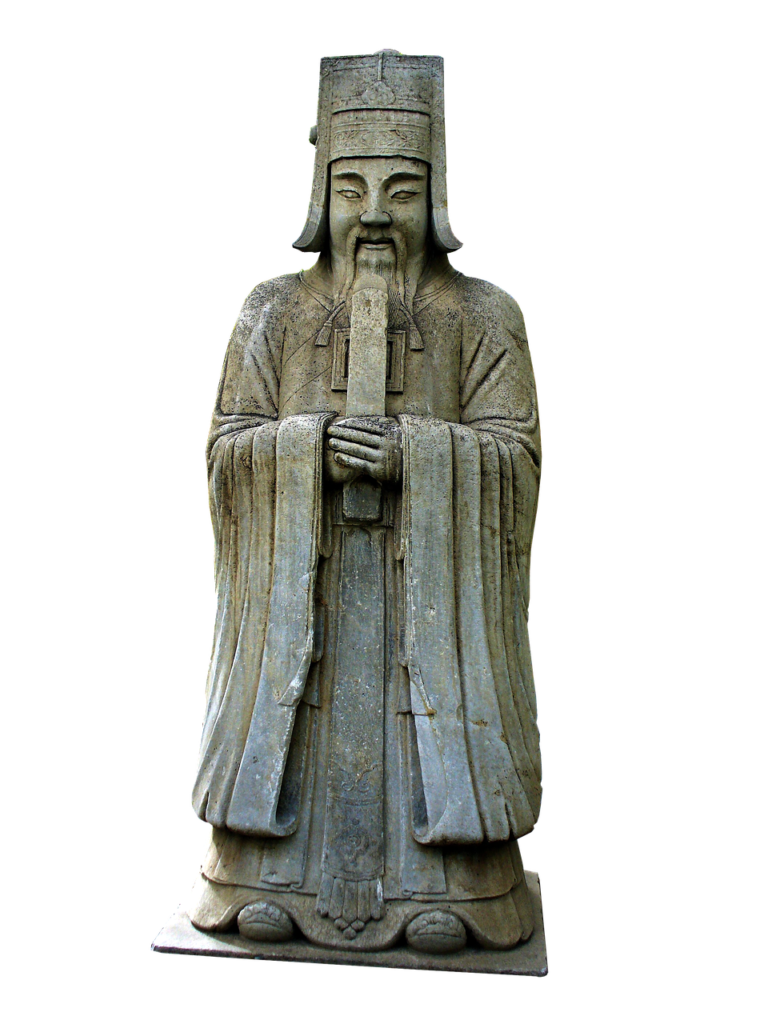



This phase encompasses several dynasties, including the Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC), known for the first unification of China under Emperor Qin Shi Huang, and the Han Dynasty (206 BC-220 AD), a pivotal period for Chinese culture, technology, and trade along the Silk Road.
Medieval China


Following the collapse of the Han Dynasty, this period saw various dynasties, including the Tang (618-907) and Song (960-1279) dynasties, known for advancements in art, science, and governance.

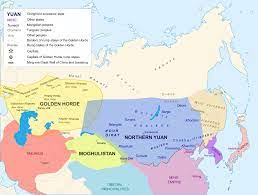
Mongol Rule and Yuan Dynasty
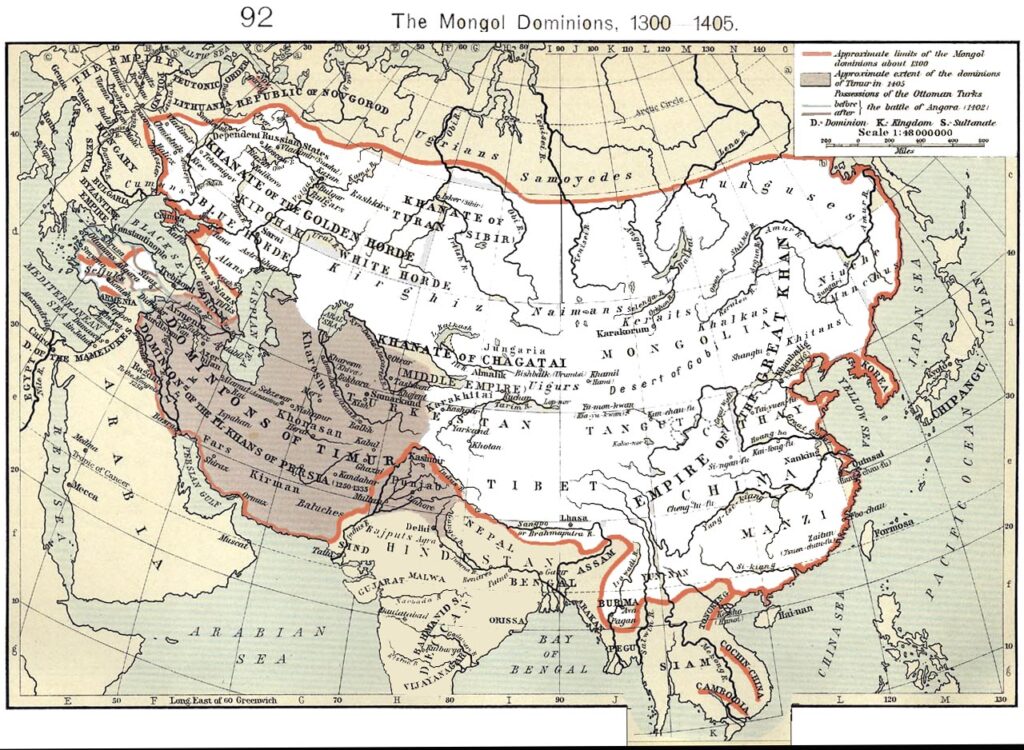
Under the leadership of Kublai Khan, the Mongols established the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368), marking a foreign rule period in China’s history.
Ming and Qing Dynasties


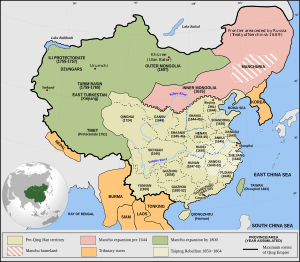
The Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) restored Chinese rule after the fall of the Mongols. Later, the Qing Dynasty (1644-1912) succeeded the Ming, ruling until the early 20th century.
Modern China



The end of the Qing Dynasty led to a period of great upheaval, including the Republican era, civil wars, and the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, led by the Communist Party under Mao Zedong.
As China strides into the future, it carries the weight of its profound history a testament to resilience, adaptability, and the enduring spirit of its people. With a gaze fixed on innovation, while rooted in ancient wisdom, China’s journey is an intricate mosaic of traditions and progress, a testament to the enduring legacy of a civilization that has weathered the tides of time. As it navigates the complexities of the modern world, China’s history remains an integral part of its identity, shaping its path forward while honoring the treasures of its storied past.







